Endolesional ablation of xanthelasma using microfiber optic laser delivery
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Accepted: 23 August 2023
Authors
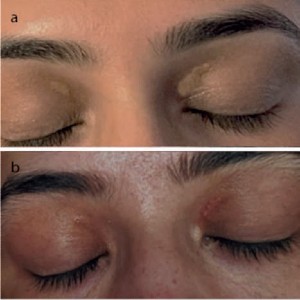
Xanthelasma palpebrarum is the most common type of cutaneous xanthoma and is often a cause of psychological distress and aesthetic dissatisfaction. The extent, depth, or background skin type, intolerance to downtime, or cost, may restrict the treatment options, or contribute to a recurrence rate of up to 60%. 1470 nm microfiber laser is a recent clinical innovation that allows highly targeted delivery of Laser to deeper tissues through fibers as small as 150 μm in diameter, targeting fat and/or water chromophores. We report a retrospective data series on five patients (10 eyelids) treated with intralesional microfiber laser, where other treatment methods were inappropriate, contraindicated, or declined. Single-use tip firing microfibers (150-300 μm), were introduced into lesions under tactile and visible indicator light guidance (1-2 W; 250-500 Hz, LEED 1-2 Jcm–2, 1470 nm ). Results were followed up with before/after photography. The pain was measured using a prevalidated 1-10 Likert scale. Patients were followed up by remote consultation up to one year post-treatment. Xanthelasma size was (7 mm ± 4 mm, mean ±SD). The average time to complete resolution was 12±2.4 weeks ( All patients were normolipidemic pre-treatment. Sessions needed were 1.2±0.4 (mean ±SD). Maximum discomfort on a 1-10 Likert scale was 3±1/10 (mean ±SD), at eight weeks’ follow-up. No recurrences were reported up to 1 year’s follow-up. No patients had visible scarring. Most importantly, all patients reported minimal downtime and could continue normally with activities of daily life. 1470 nm microfiber laser is a promising method for the management of palpebral xanthelasma: within this case series was safe and effective in experienced hands. Further, larger studies are in hand to assess follow-up long-term outcomes and patient satisfaction.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.